Maintenance Matters - Guide to Transformer Inspection and Maintenance
Introduction
Check the fan by operating it on Auto/Manual using the control switch
Check and ensure that the fan rotates freely and at full speed within approximately 5 seconds
They should rotate smoothly with minimal vibration
Check to see if there are any defects
Check for debris and scratch on the fan paint and physical defects
Listen for noise as the fan runs
If there is noise, check the bearings of the fan
If the cooling system is equipped with the pumps as well then examine the pump valves for evidence of leaking around the gland seals
Tighten the gland nut if necessary.
Gauges:
Check the temperature gauge readings on the transformer and record them
Check the ambient temperature and record it. Confirm that the temperature is within the normal operating temperature, but if it is normally high, carry out further investigations to find out why the high temperature
Check the KVA or MVA load on the transformer and record it. Ensure that the transformer is not loaded beyond its capacity
Check the oil level readings to ensure that there is no possible leak. If there are signs of a leak, carry out a pressure test. Transformer leaks must be repaired immediately to prevent further leaks, ingress of moisture and damage to the transformer
When adding oil if needed, add only the same type of oil that is in the transformer
Paint Condition:
Inspect the exterior paint for peeling, cracking, or corrosion
Repaint as needed to protect against environmental factors
Properly inspected and maintained transformer coating ensures an increased lifespan of a transformer as the tank metal will not be exposed to weather conditions for it to degrade, which could cause a leak of the oil
Note the paint conditions as good, fair, or bad
Bushing Terminals:
If the transformer is energized and on load, check the temperature of the bushing using a thermal imager (e.g. Fluke TiX590 Infrared Camera). If the temperature reading is high, then there is a loose or dirty connection at the terminals
If the transformer is not energized, use a torque measuring tool to make sure terminal connections are tight
If connections are not tight, maintenance need will include cleaning, applying contact grease and tightening connectors
Record your findings
Gaskets:
Inspect visually gaskets for wear and tear, ensuring a proper seal
Replace gaskets as necessary to prevent oil leakage
When replacing a gasket, carefully clean mating surfaces to remove any rust, dirt, transformer oil, or other contamination that might prevent a good seal. Use an appropriate gasket cement when installing new gaskets
Do not reuse old gaskets
Six months after replacing a gasket, check and retighten if necessary
Rust Prevention:
During
inspections, check all metallic parts of the transformer tank body for
rust and degradation, starting from the tank to the radiator fins to the
fans to the chassis and all parts of the tank body. Transformer should
be regularly inspected for the rust.
Cover, Joints, and Bolts:
Inspect the cover and joints for tightness and integrity
Ensure that there is no rust on the bolts, joints, and the cover of the transformer
In order to keep the rust away, make use of petroleum jelly to rub all over the bolts
Check back every six months to see the condition of the bolts and joints, and if necessary, add more petroleum jelly on joints with little or no petroleum jelly left on them
Bushing and Surge Arrester Insulators:
Bushings and surge arresters should be clean. If the surfaces are dirty, they should be cleaned while the transformer is not energized.
Examine insulators for cracks or signs of electrical tracking and take necessary action
Replace defective insulators if found to maintain insulation resistance
Transformer Oil Level:
Monitor transformer oil levels for the main tank and OLTC to ensure they remain within the recommended range. The transformer oil gauge is shown in Figure 6 and its location is shown in Figure 6.
Top up oil as needed
Control Wiring:
The control wiring used to control the transformer should always be checked for functionality
The control cabinet and associated conduit should be inspected to ensure that weather seals are intact.
Inspect control wiring for damage or deterioration
Replace or repair wiring as required to maintain operational control
Oil Dielectric Test:
It is advisable to annually test the dielectric strength of the transformer oil. To carry out the oil dielectric test on a transformer, oil samples should be drawn from the bottom of the tank
It is important to make use of proper sampling and standard operating procedures to sample the oil from the transformer
Conduct periodic oil dielectric tests to assess the condition of the insulating oil
Silica gel Breather:
During this breathing cycle, there is a need to prevent moisture from the atmosphere from entering the transformer, which can contaminate the oil inside and lead to a breakdown of the dielectric strength.
Regularly check the breather by looking at its color
A bright crystal with a blue tint shows that the silica gel is still fit for use, while a pink color shows that the breather has absorbed enough moisture and is due for a change
On Load Tap Changer
If the transformer is equipped with a load tap changer, inspect the tap changer for proper operation
Detailed information for the inspection procedures and the frequency of inspection for the tap changer is usually supplied by the manufacturers
Conclusions
Maintaining transformers is crucial for ensuring their reliability and long lifespan as vital power system components. To achieve this, regular inspections and preventive actions in areas like cooling systems, monitoring oil levels and temperature, keeping the breather moisture-free, maintaining insulation, checking terminals for hot spot, and ensuring structural integrity are essential for peak performance. Adhering to maintenance guidelines discussed, allows power system to operate safely and efficiently, reducing downtime and costly repairs. In the end, a well-maintained transformer plays a significant role in strengthening the stability and resilience of our electrical networks, supporting the daily functioning of our society.
Courtesy :
Muhammad Hanif
Former Quality Manager, ABB Electrical Industries Co. Ltd., Riyadh, SA. Currently working with EPESOL Lahore, Pakistan as Senior Technical Manager.
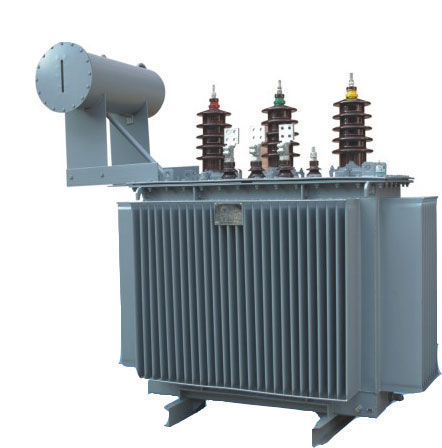
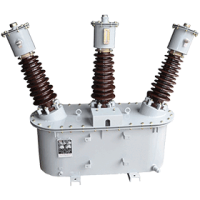
Transformer - HT Distribution
- Brand: Nano Power
- Product Code:Transformer - HT Distribution
- Availability:In Stock
-
Tk.0
- Ex Tax:Tk.0
Related Products
Digital Voltage Stabilizer
Nano Power Automatic Digital Voltage StabilizerFeatures :1)Microcontroller based circuit.2)Show..
Tk.3,000 Ex Tax:Tk.3,000
Power Factor Improvement plant
Power Factor Improvement plant : Please call us for details at : 01833059369...
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
VCB - crompton-greav es-vcb-panel
Vacuum Circuit Breaker - VCB - crompton-greav es-vcb-panel - ABB - 11KV..
Tk.325,000 Ex Tax:Tk.325,000
MIKRO POWER FACTOR REGULATOR
MIKRO - MalaysiaMIKRO POWER FACTOR REGULATORPFR140/120/80/60Microprocessor based intelligent auto sw..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
VFD - INVERTER - MOTOR DRIVE Service & Maintenance
We Service & Maintenance of all brand VFD - INVERTER - MOTOR DRIVE..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
Three Phase Automatic Voltage Stabilizer
3 phase Automatic Voltage Stabilizer - Specially for 3 phase CNC industrial equipment Intelligent l..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
Current Transformer
Working principle of the current transformer is based on the electromagnetic induction principle, ..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
ISOLATOR
Isolators:The isolators in substations are mechanical switches which are deployed for isolation of..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
Shrink-Tube
Please call us for details about goods & price :01833059369,01733115391..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
Dropout Fuse Wire - Cutout (50A~200A)
Please Call us for details & price to: 01733115391,01833059369..
Tk.400 Ex Tax:Tk.400
Surge Protector Lightning Protection 40ka4p Surge Protection Device SPD
Class II AC surge protector designed for low-voltage power supply system protection against s..
Tk.2,500 Ex Tax:Tk.2,500
PFI Capacitor
company produces Capacitors in MKP and MKV systems. Both dielectric systems are . Metal plated lay..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
LT Panel Board
We manufacture LT Panel,MBD,SDB as per customer requirement.Please call us for details : 01833059369..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
Air Circuit Breaker (ACB)
NXA Series Air Circuit Breaker - CHINT▪ Frame size (A): 1600, 2000, 3200, 4000▪ Breaking capacity: N..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
Lightning Arrester
A lightning arrester is a device used on electric power transmission and telecommunication systems..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
CRGO-EI-lamination-core
All type of CRGO-EI-lamination-core available upon request..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
Electrical Main board, distribution board, panelboard
Electrical Main board, distribution board, panel board..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
Distribution Transformer Repair And Maintenance (11KV,33KV)
Distribution Transformer Repair And Maintenance (11KV,33KV)..
Tk.0 Ex Tax:Tk.0
Tags: Transformer - HT Distribution, transformer, automation, power, energy, sub station